How does smart packaging function in the sustainability of the food supply chain? #
An effective and efficient food supply chain system can reduce the risk of food loss and food waste in the long run. Efforts to reduce food waste throughout the supply chain continue to be made with several challenges, such as inadequate infrastructure, lack of effort, regulations, and collaboration in the supply chains involved. Food loss occurs at the production, post-harvest, and storage stages, as well as the processing and packaging stages. While food waste occurs at the distribution and marketing stage, as well as the consumption stage. Causes and drivers classified as ‘Very Important’ are direct causes of lack of Good Handling Practice (GHP) implementation, technological limitations, and poor packaging/container quality.
The distribution, marketing, and consuming phases of the food supply chain contribute more to food waste. Smart packaging technologies can be useful in this area by reducing food waste and facilitating the development of a more sustainable supply chain. Smart packaging is one possible solution to reduce emissions, increase efficiency, ensure product authenticity and traceability, and prevent fraud and theft. This is supported by the benefits of smart packaging which can extend shelf life, reduce costs, improve communication between producers, distributors, and consumers, reduce losses, and increase security with a traceability mechanism that ensures food quality. These benefits extend to the supply and distribution chain, resulting in additional information beyond quality, such as product origin, location, storage conditions, and destination. Therefore, consumers or distributors have access to relevant information about product safety and quality.
How does smart packaging improve food quality, security, and traceability? #
The development of technology, materials, devices, and multifunctional sensing systems that have the potential to be included in food packaging is an effective and efficient way to ensure food quality and safety. Incorporation of devices (indicators, sensors, data carriers) and materials (scavenger and diffusion) in food packaging must comply with food categories and specifications. This suitability can provide optimal results in maintaining food quality and safety by considering the critical points of food based on the characteristics and processing used. The benefits of implementing intelligent and active packaging as part of smart packaging can be seen below.
Intelligent Packaging Benefits #
- Improving the developed HACCP and QACCP systems to:
- Detect unsafe food on time;
- Identify hazards and establish strategies and procedures to prevent, reduce or eliminate their occurrence;
- Identify processes that greatly influence quality attributes and efficiently improve the final quality of food.
- Food quality identification, monitoring, and control.
- Monitoring of gas production, temperature humidity, and growth of microorganisms
(Sources: Vanderroost et al, 2014; Ahmed et al, 2018; Ahmed et al, 2022; Alizadeh-Sani, et al 2020; Shao et al, 2021; Yousefi et al, 2019)
Intelligent and Active Packaging Benefits #
- Maintains integrity and actively stops or slows food spoilage to extend shelf life.
- Improving quality characteristics (appearance, taste, texture, and mouthfeel) and food safety
- Actively respond to modifications in product and packaging environment.
- Provide information about conditions and quality characteristics of food in real time and accurately
- Communicating with manufacturers, retailers, and consumers about product quality and safety status
- Assists in the opening of the cover and the designation of the integrity of the seal
- Ensuring product authenticity or anti-counterfeiting and fighting theft
(Sources: Han, 2013; Kuswandi dan Jumina, 2020; Ahmed et al, 2018, Ahmed et al, 2022; Janjarassakal et al, 2018; Firouz et al, 2021; Alizadeh-Sani, et al 2020; Shao et al, 2021; Yousefi et al, 2019)
How does smart packaging improve food authentication and integrity? #
Smart packaging provides solutions to ensure integrity, authentication, and traceability of where products originate, prevent counterfeiting and theft, and enhance security. This has consequences for reducing pollution, food loss, and waste in the food supply chain and provides benefits for consumers where real-time quality and extended shelf life can be provided automatically and continuously on the packaging.
What is food integrity? #
Food integrity is defined as a condition in which food is safe for consumption in terms of quality, traceability, and authenticity from various aspects, without any changes or modifications. Food safety and quality can be maintained using control and prevention in the food quality and safety system that is applied at every food processing stage. Food integrity will be achieved if the system is implemented effectively, efficiently, and continuously.
Food is also considered safe in quality and authentic, suitable with source and process claims, and ethically distributed through the food supply chain. Overall, food integrity is a continuous system that is used to avoid threats to authenticity and food security that are deliberately carried out to deceive consumers through mislabeling and counterfeiting.
What is food authentication? #
Food authentication is the process of verifying the compliance of a food product to the specifications provided on the label including country or place of origin, list of ingredients, nutritional information, production process, and brand name. Food authentication is a key system in protecting consumers and the supply chain from food fraud. Food fraud is an intentional act to replace, modify, or misinterpret food for financial gain. Food companies, manufacturers, and retailers have implemented a system to ensure food authentication to fight food fraud. The success of the system can be achieved if it focuses on the detection and prevention of all dimensions of food integrity in the supply chain. Food fraud is the result of misrepresentation regarding the integrity of products, processes, people, and data. When all aspects related to food quality, safety, authenticity, and defense are always under control through an efficient risk assessment, management, and prevention system, then food integrity can be achieved. Meanwhile, companies can be attacked by food fraud if they do not control it. Figure 1 shows the smart packaging function that facilitates the realization of food integrity and the prevention of food fraud.
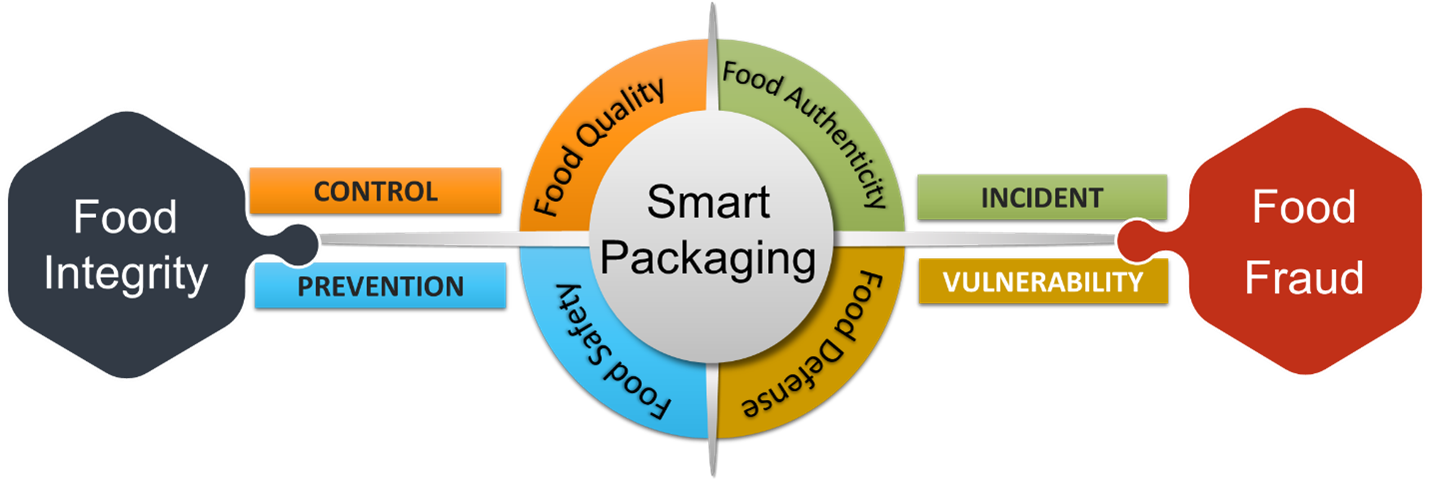
Figure 1. Smart Packaging Functionality Toward Food Integrity and Food Fraud
What is food defense? #
Food defense is a process to ensure food and beverages safety and their supply chain from all types of hazards with the motivation to contaminate food or cause supply failures. Therefore, an effective and efficient way to provide optimal protection in the food supply chain and prevent food fraud is by implementing smart packaging. Integration anti-counterfeiting is one of the strategies used to prevent, detect and control counterfeit activities, and various approaches to apply smart technologies in packaging. Intelligent packaging is part of smart packaging that guarantees the food products in the packaging according to their description and come from the brand and place of origin advertised on the label, as well as indicating the possibility of interference. The inclusion of RFID tags (devices consisting of an antenna, an integrated circuit chip, and a capacitor, which emits a signal that can be detected by nearby reading devices) can be used to minimize counterfeit food products and to assure customers of the brand and place of origin advertised on the label.
How is smart packaging used as an alternative to food preservatives and additives usage? #
The continuous development of smart packaging aims to meet the diverse needs of consumers, including:
- Improving the quality of food from a sensory and nutritional perspective without increasing the cost.
- Reduced waste and increased food safety by controlling the growth of food-borne and food spoilage microorganisms.
- Reducing the use of synthetic preservatives associated with health risks and microbial resistance.
Active packaging can meet these needs by using scavengers and emitters systems that contain preservatives, flavors, antimicrobials, and antioxidants. Oxygen scavenger (OS) and ethanol emitter (EE) in active packaging working together prevent microbiological decomposition as well as physical and chemical deterioration. The application of an active packaging system is an effective alternative to preservation technology to extend sponge cakes’ shelf life without adding chemical preservatives directly to the bakery formula. Chemical preservatives are usually used to increase shelf life. Recent food safety laws and regulations around the world as well as consumer demand for organic and healthy products with clean labels have shifted the use of synthetic chemical preservatives.
What is the consumer perspective on smart packaging? #
Understanding the cultural, social, and cognitive elements that affect customer acceptance is the foundation for the implementation of smart packaging. This can help “fine-tune” smart packaging development to meet consumer preferences and ensure effective communication regarding the application using the latest technology. Consumers still rely on expiration dates and their feelings when making food decisions. In particular, expiration dates and sensory characteristics (e.g. color) of foods emerged as major drivers of choice in stores and use/disposal of products at home. Smart labels in smart packaging can provide external validation in terms of food freshness, experience, and time needed for consumers’ readiness to fully trust labels and use them in their decision-making processes regarding food purchase, use, and disposal.
What are the challenges of smart packaging implementation? #
Smart packaging implementation faces significant challenges along with technological developments, lifestyle changes, consumer demands, and commercialization trends. Making appropriate, effective, and efficient mapping and application strategies for smart packaging is made possible by understanding the difficulties that researchers, developers, and businesses must overcome. Intelligent packaging has not been widely found in the market, due to several drawbacks including high production costs, lack of acceptance by retailers/brand owners, and high costs for research and development. The suitability of the system utilized in food products must be evaluated during the research and development process of smart packaging. Therefore, it is very important to determine the appropriate indicators or sensors for food products.
Further reading
Smart Packaging Application in Bakery Products
How to Reduce Food Waste with Food Packaging?
Potential risks of food packaging plastic waste on human health and the environment
References
Fernandez, C.M., Alves, J., Gaspar, P.D., Limaa, T.M. and Silvaa, P.D. 2022. Innovative processes in smart packaging: A systematic review. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.
Vanderroost, M., Ragaerta, P., Devliegherea, F., and De Meulenaer, B. 2014. Intelligent food packaging: The next generation. Trends in Food Science and Technology. 39: 47-62
Ahmed, I., Lin, H., Zou, L., Li, Z., Brody, A.L., Qazi, I.M., Lv, L., Pavase, T.R., Khan, M.U., Khan, S., and Sun, L. 2018. An overview of smart packaging technologies for monitoring safety and quality of meat and meat products. Packaging Technology Science., 31: 449–471.
Ahmed, M. W., Haque, M. A., Mohibbullah, M., Khan, M. S. I., Islam, M. A., Mondal, M. H. T., and Ahmmed, R. 2022. A review on active packaging for quality and safety of foods: Current trends, applications, prospects, and challenges. Food Packaging and Shelf Life 33: 100913
Alizadeh-Sani, M., Mohammadian, E., Rhim, J., and Jafari, S.M. 2020. pH-sensitive (halochromic) smart packaging films based on natural food colorants for the monitoring of food quality and safety. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 105: 93–144
Shao, P, Liu, L., Yu, J., Lin, Y., Gao, H., Chen, H., and Sun, P. 2021. An overview of intelligent freshness indicator packaging for food quality and safety monitoring. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 118: 285–296
Yousefi, H., Su, H., Imani, S. M., Alkhaldi, K., Filipe, C. D. M., and Didar, T. F. 2019. Intelligent food packaging: a review of smart sensing technologies for monitoring food quality. ACS Sensors, 4(4): 808–821
Han, J. H. 2013. A review of food packaging technologies and innovations. In Innovations in food packaging (2nd ed., pp. 3–12). Academic Press.
Kuswandi, B. and Jumina. 2020. Active and intelligent packaging, safety, and quality controls. Fresh-Cut Fruits and Vegetables Technologies and Mechanisms for Safety Control. Academic Press: 243-294
Janjarasskul, T., Tananuwong, K., Kongpensook, V., Tantratian, S., and Kokpol, S. 2016. Shelf life extension of sponge cake by active packaging as an alternative to direct addition of chemical preservatives, LWT – Food Science and Technology, 72: 166-174
Firouz, M.S., Mohi-Alden, K., and Omid, M. 2021. A critical review on intelligent and active packaging in the food industry: Research and development. Food Research International, 141: 110113
Alrobaish, W. S., Jacxsens, L., Luning, P. A. and Vlerick, P. 2021. Food Integrity Climate in Food Businesses: Conceptualization, Development, and Validation of a Self-Assessment Tool. Foods, 10: 1302.
Brooks, C., Parr, L., Smith, J. M., Buchanan, D., Snioch, D., and Hebishy, E. 2021. A review of food fraud and food authenticity across the food supply chain, with an examination of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and Brexit on food industry. Food Control, 130: 108171
Danezis, G. P., Tsagkaris, A. S., Camin, F., Brusic, V., and Georgiou, C. A. 2016. Food authentication: Techniques, trends & emerging approaches. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 85(Part A): 123–132.
Soon, J.M. and Manning, L. 2019. Developing anti-counterfeiting measures: The role of smart packaging. Food Research International, 123: 135–143
Tracey, C.T., Predeina, A.L., Krivoshapkina, E.F., and Kumacheva, E. 2022. A 3D printing approach to intelligent food packaging. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 127: 87–98
Young E, Mirosa M and Bremer P .2020. A Systematic Review of Consumer Perceptions of Smart Packaging Technologies for Food. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 4:63
Barone, A.M. and Aschemann-Witzel, J. 2022. Food handling practices and expiration dates: Consumers’ perception of smart labels. Food Control, 133: 108615





