What are the numbers we see on the eggs? #
Depending on the region and the country you are in, there are different guidelines for egg marking. For example, in the US, egg cartons with USDA-gradeshield must display the pack date. This is a 3-digit code that represents the consecutive day of the year, starting with January 1 as 001 and ending with December 31 as 365.
Regarding the classification of eggs:
Grade AA eggs represent the highest quality eggs available for purchase. These eggs are characterized by their thick, firm egg whites (albumen), high and round yolks, and clean, unbroken shells. Grade AA eggs are particularly well-suited for cooking methods like frying and poaching.
Grade A eggs, share the same exterior quality as Grade AA eggs, but their interior quality is slightly lower. In Grade A eggs, the egg whites are not as firm as those of Grade AA eggs.
Based on EU legislation, A-grade eggs shall be graded by weight as follows:
- XL-very large: 73 g and more,
- L-large: from 63 g up to 73 g,
- M-medium: from 53 g up to 63 g,
- S-small: under 53 g.
Grade B eggs, while still safe for consumption, do not meet the same standards of exterior or interior quality as Grade AA or Grade A eggs. Their egg whites are thinner, and their yolks are wider and flatter compared to higher-grade eggs. Additionally, Grade B eggs may exhibit irregular shapes and have rough or thin areas on their shells. Typically, these eggs are used in the production of liquid, frozen, and dried egg products and in various other egg-containing products.
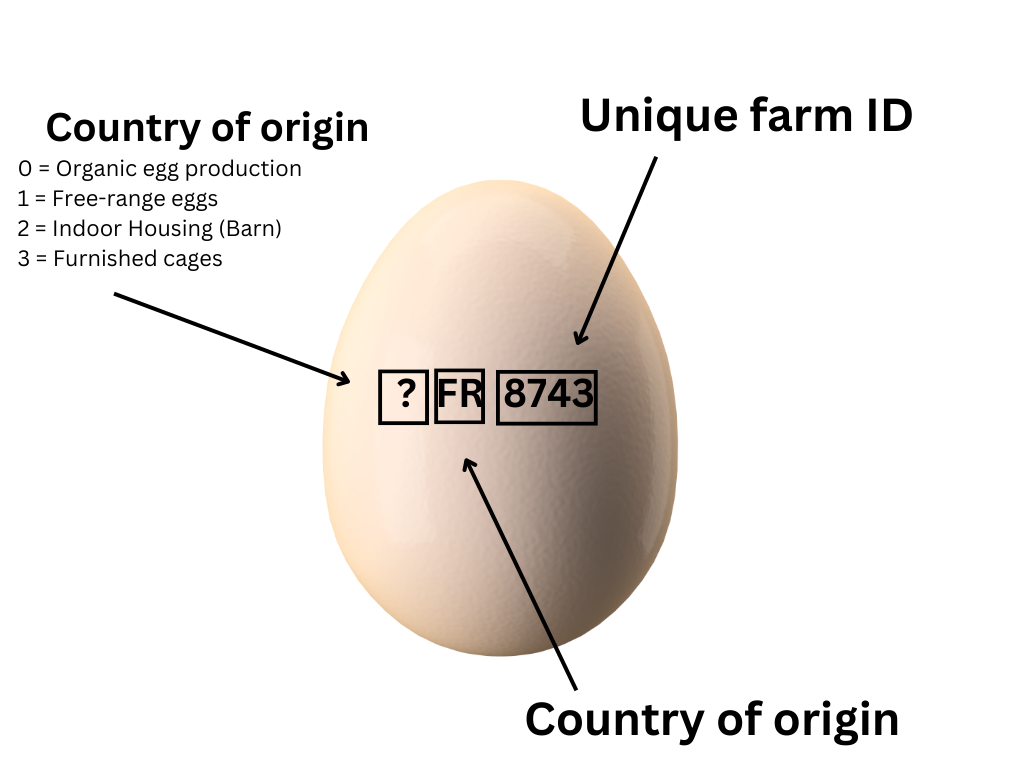
In the European Union, on every egg, you will find a tag that gives you a lot of information about the traceability of the egg. The first number is 0, 1, 2, or 3, which give us information about the production system
0 = Organic egg production
1 = Free-range eggs
2 = Indoor Housing (Barn)
3 = Furnished cages
The letters stand for the country, and the last four numbers give us the information for the farm to which the laying hens belong.
What kind of label/certification can you find on an egg? #
Cage-free are produced by hens that have the freedom to move around within a building, room, or open area that includes nesting spaces and perches.
Free-range are similar to cage-free eggs, but the hens are also given access to the outdoors.
Free-Run Eggs are sourced from hens raised in free-run housing systems, such as barns or aviaries.
Pasture-raised are laid by hens that have the opportunity to roam and forage on a well-maintained pasture.
Certified Humane: These eggs originate from facilities that adhere to specific standards for the humane treatment of farm animals, as established by the Humane Farm Animal Care Organization.
American Humane Certified: These eggs come from facilities that have completed a third-party audit and certification process conducted by the American Humane Association, demonstrating their commitment to humane animal treatment. The standards they have, cover aspects such as providing nutritious food, creating suitable living conditions, responsible management, knowledgeable care, and considerate handling, transport, and slaughter practices.
Certified Organic are produced by cage-free or free-range hens that are raised on certified organic feed.
Pasteurized eggs undergo a controlled heating process at a specific temperature to eliminate harmful pathogens.
Kosher Certified: The Kosher certification signifies that a product has been manufactured and processed in accordance with Jewish dietary regulations and complies with the stringent criteria set by the OU (Orthodox Union). This certification entails thorough inspections of the production facilities, ingredients, and production techniques to ensure compliance with kosher standards.
Enriched: These eggs are laid by hens fed a specialized diet, often resulting in higher levels of nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids (up to 10-20%).
Vegetarian-fed: These eggs are laid by hens that are exclusively fed a vegetarian diet.
Further reading
Interesting facts about eggs
Poultry Egg Types
What affects the quality and size of the eggs?
Eggs: Nutritional Value & Health Benefits
References:
USDA, https://ask.usda.gov/s/article/How-long-can-you-store-eggs-in-the-refrigerator4
Puglisi MJ, Fernandez ML. The Health Benefits of Egg Protein. Nutrients. 2022 Jul 15;14(14):2904. doi: 10.3390/nu14142904. PMID: 35889862; PMCID: PMC9316657.
Dr. Gargi Mahapatra, 2021, Factors affecting Egg Quality & Physico-chemical properties of Egg, Bihar Animal Sciences University
Chen, G.-C., Chen, L.-H., Mossavar-Rahmani, Y., Kamensky, V., Shadyab, A. H., Haring, B., Wild, R. A., Silver, B., Kuller, L. H., Sun, Y., Saquib, N., Howard, B., Snetselaar, L. G., Neuhouser, M. L., Allison, M. A., Van Horn, L., Manson, J. E., Wassertheil-Smoller, S., & Qi, Q. (2021). Dietary cholesterol and egg intake in relation to incident cardiovascular disease and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in postmenopausal women. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 113(4), 948–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqaa353





